Databases for Beginners
A beginners look at databases and how they are utilized in computer programming. Will cover topics such as Database Management Systems (DBMS), Relational Database Management System (RDBMS), Tables, Keys, Building Relations, Indexes, Queries, and SQL.
Database Basics
A database is a structured collection of records, and a database management system is capable of:
- ️add, remove and update records
- ️retrieve data that match certain criteria
- ️cross reference data in different tables
- ️perform complex aggregate calculations
Databases consist of columns (attributes) and rows (records). There are a number of advantages that databases have over spreadsheets, but in essence they allow for easier manipulation of data. Single table databases (i.e. spreadsheets) have disadvantages such as: redundancy of data, problem with complex data, problems in updating in bulk, problems in adding incomplete data, problems in removing groups of data. Relational Databases, however, offer minimum redundancy, are organized as a system of related tables, have referential integrity, utilize database keys, and invoke the ACID model (a guarantee of successful transactions):
- ️Atomicity - "the all or nothing" rule
- ️Consistency - only valid data in
- ️Isolation - order of executed transactions
- ️Durability - committed transactions will not be lost
Tables
- ️Contain a unique name
- ️Size is equivalent to the number of rows
- ️Order is equivalent to the number of columns
- ️All rows are typically different
- ️Order of rows is not important
- ️Unique headers identify columns
- ️There can be a null value in tables
Database Keys
- ️Primary Key
- ️Value is unique for each record in a table
- ️This value can not be used twice
- ️Foreign Keys
- ️Used to create relationships between tables
- ️No uniqueness constraint for foreign keys
- ️Relationship between Primary and Foreign Keys
- ️Same format
- ️Same values
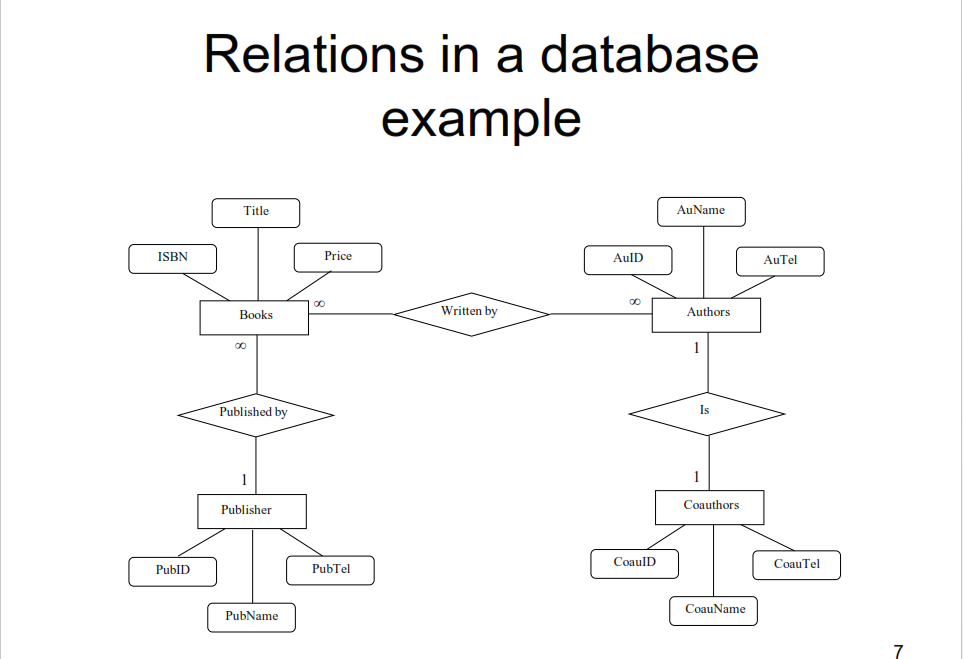
Visual examples of the relationships present in the tables of relational databases:
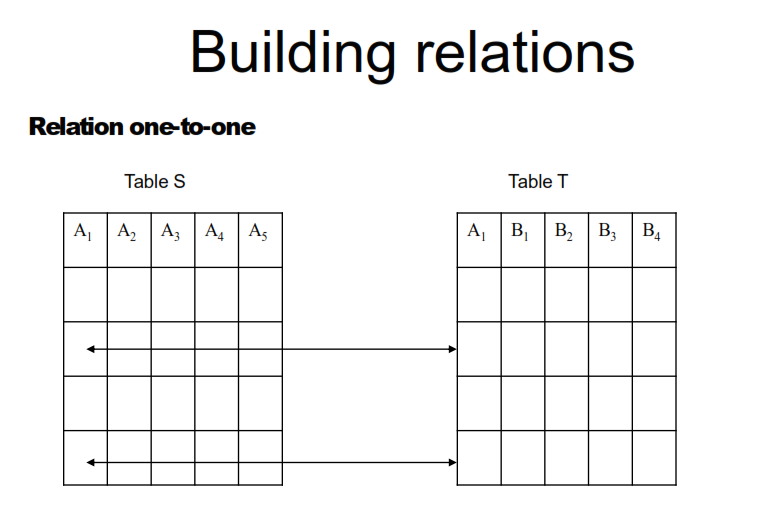
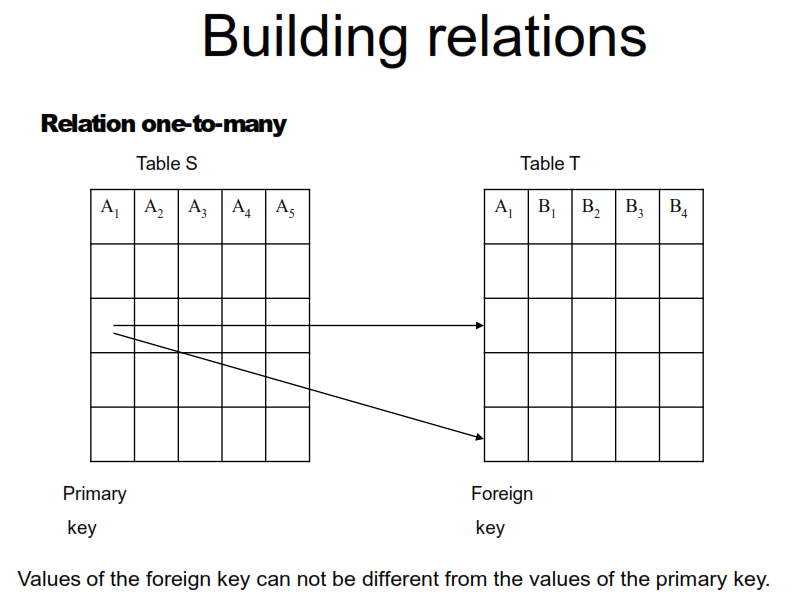
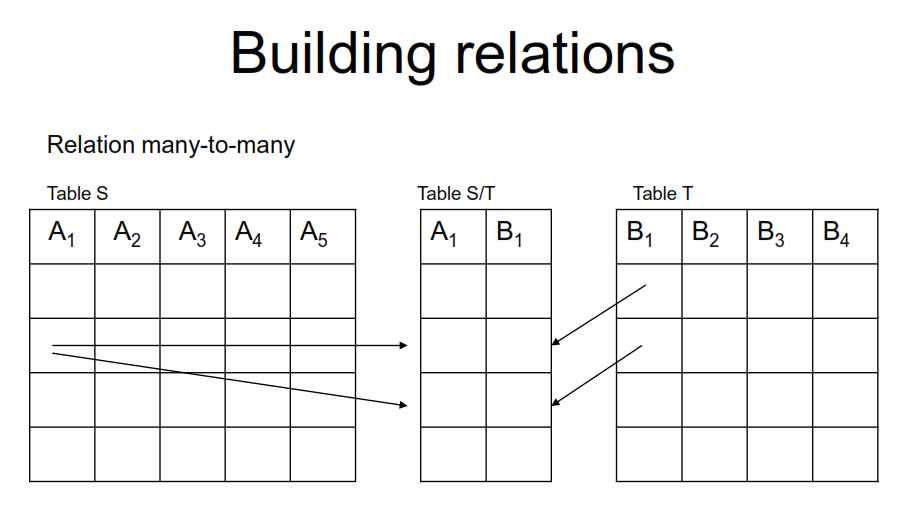
Enforcing Referential Integrity
- ️Cascade Update Related Fields - the values of foreign keys change following the changes of the values of the primary key.
- ️Cascade Delete Related Records - deleting a record from the primary field in a relationship causes a deletion of all related records in the second table
The purpose of indexing field values is to speed up the access to specific data, especially that which is utilized in large tables. Indexing field values allows you to update all indexes every time a table record is updated or added.
There are certain types of attributes or principles for building a database. These attributes are: identification, information, or identification + information.



